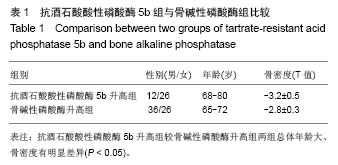
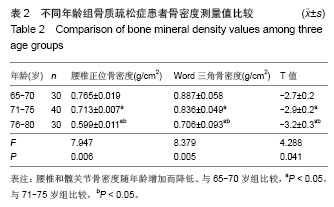
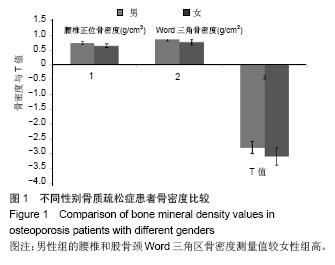
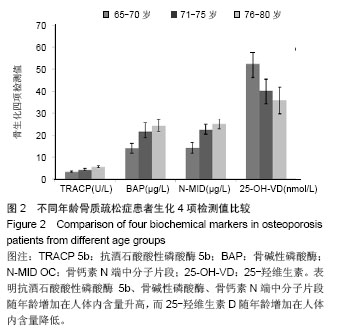
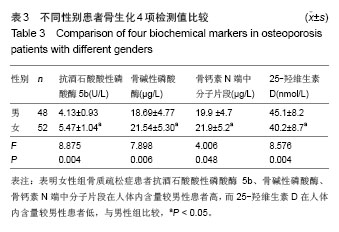
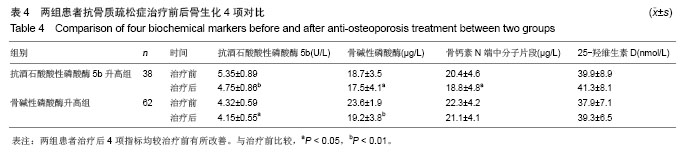
| [1]中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会. 原发性骨质疏松症诊治指南(2011年)[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2011, 4(3):2-17.
[2]Assessment of fracture risk and its application to screening for post-menopausal osteoporosis. Report of a WHO Study Group. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 1994;843:1-129.
[3]Kanis JA, Bianchi G, BilezikianJP,etal.Towards a diagnostic and therapeutic consensus in male osteoporo-sis. Osteoporos Int. 2011;22:2789-98.
[4]Schuit SC, van der Klift M, WeelAE,etal.Fracture incidence and association with bone mineral density in elderly men and women: the Rotterdam Study. Bone. 2004;34:195-202.
[5]张萌萌.骨重建中的骨代谢指标[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,8 (19):866-873.
[6]Gallacher SJ, Dixon T.Impact of treatments for postmenopausal os-teoporosis (Bisphophonates, Parathyroid Hormone, Strontium Ranelate and Denosumab) on bone quality: a systematic review. Calcif Tissue Int. 2010;87: 469-684.
[7]Kanis JA, Johnell O, Oden A,et al. FRAX and the assessment of fracture probability in men and women from the UK. Osteoporos Int. 2008;19:385-97.
[8]Vasikaran S, Eastell R, Bruyère O, et al. Markers of bone turnover for the prediction of fracture risk and monitoring of osteoporosis treatment: a need for international reference standards. Osteoporos Int.2011;22:391-420.
[9]Kanis JA. Diagnosis of osteoporosis and assessment of fracture risk.Lancet.2002, 359:1929-36.
[10]Cosman F, Lindsay R, LeBoffMS,et al. National Osteoporosis Foundation. Clinician’s guide to prevention and treatment of osteoporosis 2013.
[11]Rodrigues AM, Caetano-Lopes J, Vale AC,et al. Low osteocalcin/collagen type I bone gene expression ratio is associ-ated with hip fragility fractures. Bone.2012;51:981-9.
[12]Rodrigues AM, Caetano-Lopes J, Vale AC,etal.Smoking is a predictor of worse trabecular mechanical performance in hip fragility fracture patients. J Bone Miner Metab.2012;30:692-699.
[13]Epstein S.The roles of bone mineral density, bone turnover, and other properties in reducing fracture risk during antiresorptivetherapy. Mayo Clin Proc.2005;80(3):379-388.
[14]Liu Zhonghou. The diagnosis of osteoporosis. Hong Kong:Chinese modern literature and Art Publishing House. 2011:452-465.
[15]Civitelli R, Armamento-Villareal R, Napoli N. Bone turnover markers: un-derstanding their value in clinical trials and clinical practice. Osteoporos Int. 2009;20:843-51.
[16]张萌萌,李亚刚,高远,等.834例女性CTX-1、TRACP、BGP、BALP水平与BMD相关性研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2012, 18(9): 795-797.
[17]Garnero P, Sornay-Rendu E, Claustrat B,et al. Biochemical markers of bone turnover, endogenous hormones and the risk of frac-tures in postmenopausal women: the OFELY study.J Bone Miner Res.2000;15:1526-1536.
[18]施鸣,范璐,陈新.骨代谢标志物与骨质疏松的相关性研究[J].标记免疫分析与临床,2012,19(6):351-353.
[19]LiuZhonghou. The diagnosis of osteoporosis.Hong Kong: Chinese modern literature and Art Publishing House.2011: 452-465, 520-523.
[20]孟晓林,马东亚,王春,等.注射用骨肽联合阿仑膦酸钠治疗骨质疏松症的临床研究[J].实用药物与临床,2012,1(8):490-491. |